Depreciation: What it means and how to calculate it
April 20, 2023What is depreciation?
Functions of depreciation
Depreciation expenses (cost of doing business)
Depreciation and tax
Depreciation on your balance sheet and valuing your business
What is a depreciation schedule?
How to calculate depreciation
Straight-line depreciation method

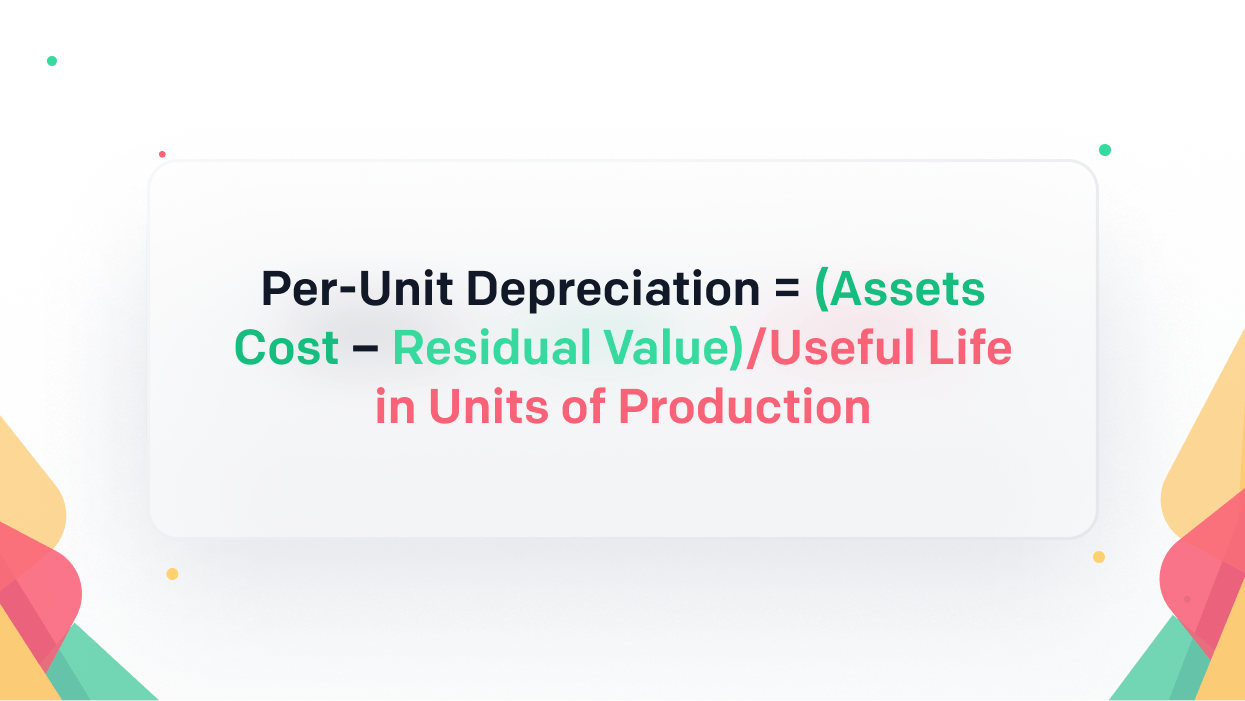
Unit of production depreciation method

Double-declining balance depreciation method






